Well that’s exactly what happened when researchers gave patients 1 tablespoon of this weird “gelatin.”

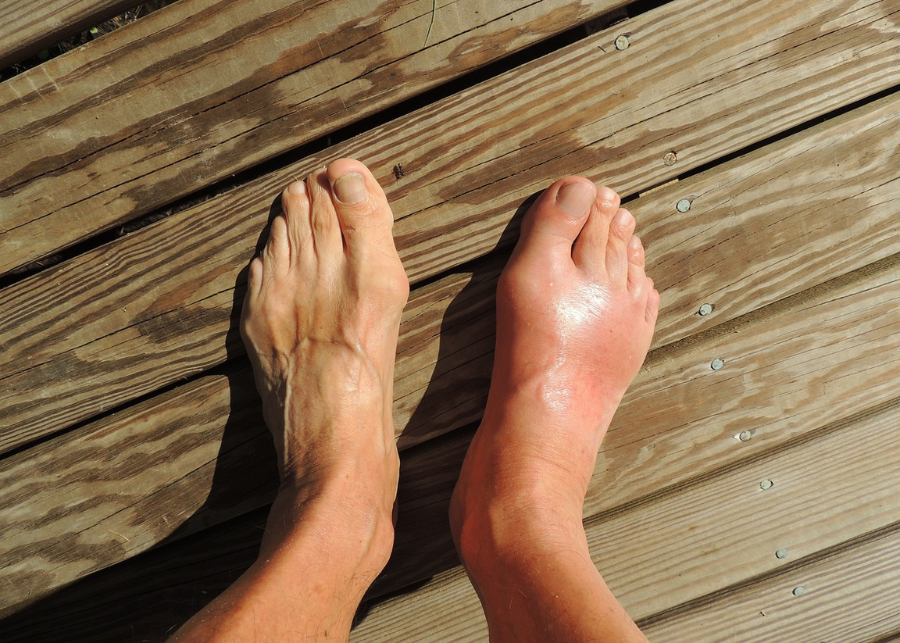
Have you ever woken up with sudden and intense pain in your big toe or another joint? If so, you may have experienced gout. Today, I will talk about one of the most common types of arthritis, which is gout. Gout is a painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this video, I will review five signs of gout you need to know about, including some lesser known symptoms. Plus, we will dive deep in what can precipitate a gout attack.
So let’s get started. Rheumatologist oncall.com I want to share with you a story of one of my patients. One morning, Mr. Colleen called my office for an urgent appointment. He told my assistant that he needed to be seen right away as he was in excruciating pain. He had swelling in his right foot and he could not walk. He could not even stand the sheets over his foot. When he came to my office, Mr. Colling hopped on 1ft. He had a red, swollen, red foot, and he could not even stand to be examined.
A few days before he came to me, he attended a party where he drunk some alcohol and ate some shellfish. At this point, I was almost sure I knew what he was experiencing. But watch until the end to find out what happened to Mr. Choline. What is gout? Gout is a very common form of inflammatory arthritis, which is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in your joints. It will affect males earlier in lives, but after menopause, females are also affected.
Gout is very rare in children. The uric acid crystals can cause inflammation, redness and pain in certain situations. While most patients experience gout in the big toe, some patients will get gout in the hands, in the knees, in the ankles, and even the lower back, like the sacroeliac joints. So not always gout starts in the big toe. You can have one joint affected, or you can have multiple joints at the same time.
And you can also have migratory pain, meaning that one joint will hurt this week, and then a few days or weeks after, you will have another joint affected and in another few days, another joint affected. Now let’s talk about five signs of gout that you need to be aware of. Podagra. Podagra refers to the gout that involves a big toe. If you have gout in the big toes, you will experience redness, pain, swelling and intense pain. Most of my patients say that it’s the worst pain in their life, worse than giving birth.
Most patients go to bed fine and they wake up in severe pain the following day. The pain may last for several days and can go away on its own, but it can also respond to antiinflammatory medication. Before seeing the doctor. Most patients will try something for pain, which is most often overthecounter antiinflammatory medication like naproxen and ibuprofen. Ankles, knees, elbows, wrist and fingers can all be involved.
Most of the time, one joint at a time is affected. But as I mentioned, multiple joints at a time or a migratory type of pain can happen. The joints will be red, swollen and very painful. I cannot emphasize that patients can be tearful due to severe pain. Tofi tofi are small white and yellowish lumps that can develop under your skin. They are caused by the accumulation of these uric acid crystals in your joints, but it can also be a sign of advanced gout.
When I have a patient with gout, I always examine the ears, the elbows and hands, as these are the common areas for tofi. Tofi do not hurt, but they can damage your joints. They can open up the skin in the areas where they are located, and they can increase the risk for infections. There are patients with huge TOFI that can cause severe destruction of the joints and can affect the mobility of those joints. Kidney stones.
So kidney stones are caused by the buildup of the uric acid crystals in your kidneys. Once the kidney stones are big enough and they start to mobilize, they can cause severe pain on your side or on the back, together with nausea and vomiting. Kidney disease or chronic nephropathy. This is a way to call a kidney disease that is caused by uric acid deposits in the kidneys that will create inflammation and eventually will lead to kidney damage.
You must know that gout is often linked to other medical conditions like obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes. Some medications like diuretics or water pills, low dose aspirin medications to decrease your blood pressure, and some chemotherapy drugs can also increase the uric acid and precipitate a gout attack. What happened to Mr. Colin? Mr. Colin was a gentleman that was slightly overweight, and he was often eating in restaurants while he was meeting with his clients. He preferred a beef, a hamburger, and he also had a whiskey every night before dinner.
His father also had gout. He was familiar with this disease. After his episode of Gout, we decided to get some labs. And then I started him on treatment, first on steroids, then with a medication that will lower his uric acid. After a few days on steroids, he called back that his swelling is down, his foot was no longer red, and hot and he was able to put weight on that foot. He called me his angel for helping him with that awful pain. In conclusion, gout is a very painful type of arthritis that is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in your joints.
The five signs of gout will include podadra, other joints involvement, tofi, kidney stones, and kidney disease. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should call a rheumatologist to get evaluated immediately. It is better to prevent gout attacks than experience one. If you don’t believe me, I ask someone that had a gout attack and remember to leave me a comment and share your gout story with me.
Today we’ll talk about gout. It’s an inflammatory arthritis. It affects your freaking big toe, aka your first metatarsophalangeal joints. Risk factors include meat, beer, being a male, especially around age 40. Historically it was known as the disease of kings because if you could afford a steak and a beer, you had to be really rich first. Let’s go back to square one. Joint diseases are either noninflammatory, inflammatory, septic or hemorrhagic.
Where does gout fit? It’s an inflammatory. Freaking arthritis. Would you classify gout with the osteo as noninflammatory or with the rheumatoid as inflammatory? It’s with the rheumatoid as inflammatory. And therefore the word osteoarthritis is a wrong freaking name because there is no inflammation. Honestly, there might be a little bit of inflammation, osteoarthritis, but it’s not the cause, it’s not the trigger of the freaking disease.
Please watch my previous video videos in this playlist. And today is the 65th video or something. Gout is here with the inflammatory. Other inflammatory include rheumatoid, lupus, seronegative, spondylo, arthropathies. You remember the mnemonic pear and I don’t care, Joe Green syndrome and septic arthritis. That’s a freaking emergency. Rheumatological diseases happen to be noninflammatory or inflammatory. Noninflammatory, such as osteo.
There are no cardinal signs of inflammation. Yeah, because it’s noninflammatory, it’s asymmetric. Worse in the evening, ESR and CRP are within normal limit inflammatory, such as rheumatoid. However, you have the cardinal signs of inflammation. Redness, hotness, swelling, pain, loss of function. It’s symmetric because rheumatoid arthritis is polyarthritis. However, gout, which is today’s topic, is mono. Freaking arthritis. If it’s mono, it’s going to affect one joint. It has to be asymmetrical. Sorry. And ESR and CRP are expected to be high.
Speaking of ESR and CRP, these are acute phase reactants. They correlate with disease activity, they correlate with response to therapy, but they have no diagnostic value. Just because your ESR is high doesn’t necessarily mean that you have gout. Get your head out of your sphincter. Both ESR and CRP are more sensitive than specific. You cannot diagnose gout based on ESR or CRP. Rheumatological disease, monoarticular, oligo, or poly.
What do you think gout is? Gout is monoarticular, usually one joint. It’s usually the first metatarsophalangeal joint, your big toe. Rheumatological diseases either involve the dip, which is here, distal intraphalangeal joint, MCP, and rest. So here is the MCP, metacarpophalangeal and wrist, or first metatarsophalangeal MTP. Gout is here first mtp. Osteo can also affect the first MTP. Also, you know what septic arthritis can affect the first MTP.
Arthritis are either acute or chronic. What do you think gout is? Gout could be either one. It could be acute. We call this acute gouty arthritis or acute gout attack. Or it could be chronic. We call this chronic tofacious gout. Arthritis is either asymmetric or symmetric, of course, gout. Since it’s monoarticular, it affects only one joint. It has to be asymmetrical. Gout is a crystalline arthropathy. What does that mean? Inflammatory arthritis caused by deposition of microscopic crystals into joints and other tissues. Most of the cases it’s just joints.
Sometimes it’s joints and other tissues, muscles, tendons, and even the kidney. We call this urate nephropathy or urate crystallopathy. Types of crystalline arthropathy. Based on the course and based on the crystals, based on the course, acute or chronic? Based on the crystals could be gout. Pseudo gout or pseudo pseudo. This is like a doofus name. The actual scientific name is hydroxyapatite arthropathy, or haa.
In the past, in the good old days, which were not so good, hydroxyapatite arthropathy was part of the pseudogout. But now they have separated the classification because these diseases are not the same. If your textbook still has hydroxyapatite arthropathy as pseudogout, it means your textbook has been written by an old dinosaur. Gout. What are the types of the crystals? They are called the monosodium urate. How about the pseudogout? Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals. CPPD disease, man. Pseudo pseudo hydroxyapatite arthropathy.
It has to be hydroxyapatite crystals. Joint disease, either axial or peripheral. Gout, of course, is peripheral. Your first metatarsophalangeal joint is peripheral. Is it a big joint or a small joint? Of course it’s a small joint. Is gout an autoimmune disease? Oh, shut up. It’s not an autoimmune disease. By the way, here is a hint. Autoimmune disease are usually commoner in females. Gout, which is not an autoimmune disease, is commoner in males. So let’s get our act together. Gout is inflammatory arthritis.
It affects the first metatarsal or metatarsal phalangeal joint. Your first MTP gout is monoarticular, therefore it’s asymmetrical. It could be acute or chronic as a joint disease. It’s peripheral and it’s non autoimmune. It’s commoner in males. What is the definition of gout? Just cram the aforementioned bits of information together and you have a perfect definition. Gout is a crystalline, inflammatory, asymmetrical monoarthritis. By the way, this monoarthritis could be primary or secondary, acute or chronic due to overproduction or under excretion of uric acid.
It involves small peripheral joints, specifically the first metatarsophalangeal joint, aka my big toe. Why? Due to deposition of crystals, no microscopic crystals. And they are specifically monosodium urate or msu, more common in males than females. The ratio is about four to one. Please do not confuse hyperuricemia with gout. That’s a very common mistake among students. Just because your uric acid in the serum is high does not necessarily mean that you will suffer a gouty attack.
And just because you have a gouty attack right now doesn’t necessarily mean that uric acid level is high. Gout is inflammatory, it’s commoner in males. Inflammatory therefore there is pain on swelling, cardinal signs of inflammation. Redness, hotness, swelling, pain, loss of function, conscious, your symptoms. Gout is one of the causes of fever. Gout can affect small joints. Pain at night usually awakens the patient from sleep. Also pain on trauma.
You know when you keep wandering around the house while being barefooted and then you hit your little toe into the sofa. Oh, it hurts. In gout, it hurts ten x and then it’s a chronic disease. Sometimes with acute flares. During the acute flares, they are called acute, so you’ll find neutrophils. And since this is an inflammatory freaking arthritis. If you aspire the joint, if you aspire the big toe, you’ll find white blood cells between 2100 thousand, some authors say between 2070 5000. I couldn’t care less if it’s inflammatory. Expect to see elevation of ESR and or CRP.
Now, here is a case for you. Please try to answer it now. Please pause. Let’s dissect that. Homer Simpson, a 42 year old male, came at 03:40 a.m., screaming, right? Big toe pain. That’s nine out of ten. That’s big time pain. The pain started 20 minutes ago and awakened him up from sleep. He just had a beer party yesterday and drank two cases of beer. The steak and sushi were delicious. Steak and sushi don’t mix. He has a history of hypertension and diabetes.
On physical exam, his right big toe is warm, red, swollen, and tender. Number one, what’s the most likely diagnosis? Two, what’s the next best step? Three, if left untreated, what’s the most likely fate of this acute attack? So what’s the most likely diagnosis? This is easy. This is acute gouty freaking arthritis. What’s the next best step? That’s a very important question. If you say observation and follow up. Shut up. The pain is nine out of ten. Just send the patient home.
Just stop it. Serum uric acid level. Again, hyper urecemia is not the same as gout. Just because you have an acute gout attack right now doesn’t necessarily mean that the serum uric Acid level is going to be high. Actually, usually normal or even low. Give nsaids. Yeah, but you have to confirm the diagnosis first. And more importantly, you have to rule out septic arthritis first. Septic arthritis is a freaking emergency. Again, you have to confirm the freaking diagnosis, and you have to rule out the septic arthritis. So the correct answer here is e arthrocentesis with joint fluid analysis. What’s the purpose of arthrocentes and joint fluidness? Oh, yeah, to diagnose gout. Oh, shut up.
Who cares about gout? Number one, to rule out septic arthritis. And then to rule out septic arthritis. And then to rule out septic arthritis because it’s a freaking emergency. And then four, to diagnose gout. Number three, if bluffs untreated, what’s the most likely fate of this attack? Death from pain. Oh, this is drama queen transformation to a chronic disease. It’s not like this is hepatitis. Death from a septic shock. Calm down. Self resolves within a few days.
That’s the correct answers. Does that mean that we are not going to intervene? Of course we are going to intervene. We’re going to give the patient nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs to control the pain. But this is not the question. Risk factors of gout. Male. Just being a male is a risk factor. Usually between 30 to 45 years of age. Hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia. Alcohol use. Okay, there are three types of alcohol. Beer, wine and liquors.
Which ones? Usually beer. This is the number one. And of course, wine is very, very unlikely. Liquor, slightly likely. So it could be. But beer is the big. In other words, like Germans, not French nor Irish. That’s a terrible joke. I’m so sorry. Forgive me. I’m just trying to help you memorize stuff. I love you all. Consumption of fatty Food, red meat, organ meat, seafood, including sushi. Some people say even soft drinks. And anything that contains fructose.
Trauma. And we’ll talk about that soon. Surgery, starvation or dehydration. Drugs? Such as what? Diurex? All of them? No, the most commonly used ones. Loop. Antiazine. Aspirin at high dose or low dose? Low dose. You mean the antiplatelet aspirin? Absolutely. It’s 81 milligrams in the United States. In the UK, hey, it’s slightly different, but it’s a low dose. Niacin. Low or high dose? High dose. You mean the antilipid niacin or nicotinic acid or niacinamide or nicotinamide.
Absolutely freaking luthie. Remember that aspirin at elodose is antiplatelet. At a high dose, it’s antifreeking, inflammatory. But niacin at a low dose, it’s a vitamin. Which vitamin? B. Three. Is this fat soluble or lipid soluble? I’m sorry? Is it water soluble or fat soluble? It’s water soluble at high dose. Niacin is a lipid lowering drug. Cool. Tuberculosis medications such as pyrozanamide, chemotherapy, such as cyclosporin and tecrolomus.
These two are immunosuppressants. Gout is not common in pre menopausal women. Why not? Because estrogen is eureko sewic. I love this name. Urico means uric acid sew from urea. So it lets the uric acid into the urine. So rheumatoid was commoner in women. Gout is commoner in men. Etiology of gout could be primary or secondary. What’s the most common one? Secondary. What is primary? It’s like the patient was primarily born this way.
It’s an inborn error of uric acid metabolism or purine metabolism. How about secondary? It’s secondary to something else. It could be secondary to overproduction or under excretion. Of what? Of freaking uric acid. Let’s start with primary inborn error of uric acid or purine metabolism, such as Lisnian syndrome. This is a deficiency of hgprtase enzyme hypoxanthine, guanine, phosphoribosil, transferase. Ooh. Glycogen storage diseases. Secondary.
Increased production of purine or uric acid. Decreased excretion. Why would I increase production? First, I will let you know that any cell, any cell has a nucleus. Not like, except rbcs, okay? And except platelets, because they are not even cells. And then they have dna and after that, in the dna, you have purines and primidines. We are talking about the purines. When you metabolize purines, you get freaking uric acid.
So let’s say the patient has leukemia and you are giving the patient chemo. Leukemia is proliferation, proliferation, proliferation, chemo. They will die and die, and die. And then they will proliferate and die, proliferate and die. This is called rapid filter. And over. Of course it’s going to produce purines and uric acid. Tumor lysis syndrome. Again, proliferation and death, proliferation and death. You produce lots of uric acid. Hashtag gout. Mpns. What is mpns? Myelopoliferative neoplasm proliferate and die. Hemolytic anemia, same thing.
The bone marrow is working like crazy. Psoriasis. There is increased epithelial turnover. This was number one, which is increased cell turnover. Also, g six PD deficiency can have gout. Fructose ingestion can also lead to gout. Remember the sugary drinks? Yep. For that reason, secondary due to under excretion. Under excretion, by the way, is more common than overproduction. Such as what? Under excretion, you can blame the kidney.
Nephropathy, lead poisoning, which trashes the kidney. Alcoholism, which can affect the kidney. Ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis. These are two types of high anion gap. Metabolic acidosis. Beer, red meat, seafood drugs such as diurects, aspirin, niacin, tb drugs and chemotherapeutics. Remember the myelopoliferative neoplasms and the lymphopoliferative neoplasms? We have talked about them before. Some disease are associated with gout, including kidney stones.
But I did not go to medical school for many years in order just to say kidney stones. I will leave that to the layman peasants. I’m just an elite sophisticate. I’ll say urate. Nephrolithiasis, crystallopathy or nephropathy. I’m super sophisticated to the point of being stupid. What difference does it make? Nothing. Hypertension, lead poisoning, interstitial nephritis, which will lead to decreased uric acid secretion, which will lead to accumulation of uric acid in your plasma. By the way, one and two are very interesting cases.
Why? Because when you have a patient who has lots of uric acid and kidney problem, you are not sure. Did the uric acid was high first and then trash the kidney? Or was the kidney screwed up first and then raised the level of uric acid in your plasma. There is no way of knowing. It’s very hard unless you know the patient’s history. Hypertension, same thing. Hypertension can trash your kidney. Also, a bad kidney can cause hypertension.
Don’t get confused, my friend. Hyperecemia is not the same as gout. I’ll prove it for you. More than 75% of patients with hyperecemia are asymptomatic. There is no gout, there is no pudaggra, there is no tofi, there is no nephropathy. There is no correlation between uric acid level in the plasma and acute gouty arthritis. Oftentimes during acute gouty attack, serum uric acid will be normal or even low. Imagine that. So what does a high plasma uric acid mean?
It means that the patient is at risk. Does that mean that they have to get gout? Oh, shut up. They’re just at risk. Correlation is not the same as causation. It does not confirm the diagnosis of gout. You need to aspire the joint and see the crystals under the beautiful plain polarized microscopy. Signs and symptoms of gout. Let’s start with acute gout. Acutely tender, warm, red and swollen. These are the cardinal signs of acute inflammation. Joint.
Which joint? First, metropholangeal. This is the big toe. This is called podagron. And sometimes it’s not the big toe, it’s the knee. Okay, how does the pain starts? Like this. Pew. Very severe. It peaks about 24 hours from the start, and then give it a few days and it’s going to subside on its own. But of course, we’re not going to leave the patient with pain, like ten out of ten. We should give them pain medications. Patient is asymptomatic between the attacks. So this is an acute attack.
A peak, and then the patient is asymptomatic, and then another peak, and then the patient is asymptomatic. Contrast that with chronic gout, which is tofacious gout. There are symptoms in between the attacks. And this is how we differentiate between acute gouty arthritis and chronic gout. But of course, some patients have chronic gout that has some flares. Gout can cause five conditions. You can be asymptomatic with high uric acid. I’ve told you, high uric acid is not the same as gout.
Acute arthritis, that’s painful, intercritical period with no pain symptoms. Chronic tofacious gout. Those are the tofi. Those are hard as rocks. Uric acid, nephropathy, stones in your kidney. Have you ever wondered why does acute gout affect the first MTP joint? Why your big toe? To answer this question, we have to go back to chemistry. Bring a flask and this flask has some kind of solution. And then start scratching the flask and then it will crystallize.
What, like crystal formation just by scratching it? Yep. How come? You have formed a nucleation point and then the surrounding molecules will gather around it and then they will precipitate in the form of crystals. So what does that have to do with gout? Remove the flask and put your big toe, your first mtp when you scratch it. What do you mean by scratch it? I mean, look at your big toe. It’s a weight bearing joint. Your entire body weight is standing upon your big toe.
So of course this is a nucleation point. That’s why crystals happen in your big toe, honey. And that’s why trauma is a risk factor, remember? Yep, because trauma creates a nucleation point. Oh, medicine is just so hard and it’s boring and doesn’t make any sense. Oh, shut up. It’s just that your professor is so fake and he got his calvarium stuck all the way up his physiological sphincter. You’ll find it stuck in the splenic flexure soon.
Medicosis compilations flasks in medicine a flask shaped ulcer. This is anemoeba histolytica. Histolytica. It destroys your tissue, causing bloody diarrhea or bloody stool. Erlen Meyer flask bones. You see that in osteo, not porosis, but petrosis. And by the way, petra means what? Petra means rock. And that’s why the name Peter means rock. And in Jordan, there is a tourism destination called petra. It’s just a huge rock in Jordan with miticosis.
Medicine and history just makes sense together. If you love my videos, I have a cardiac pharmacology premium course on my website. Go to medicosisperfectionalities.com. It has 50 videos and it’s on sale right now. In the next video, talk about diagnosis and treatment of gout. What’s the difference between podagra and tofi? Podagra, like pilgra. What does pilagra mean? Pella means skin and agra means seized. Your skin has been seized. Pilas agras.
But podagra, your big toe has been seized. That’s literally what. How about tofi? It means stones. Podagra is seen in acute gouty attack or gouty arthritis. What’s the most common location first metatarsophala and children. What’s the second common? Urine. This is acute therefore neutrophils. Tofi stones. These are like hard as rocks. Chronic gout baby chronic topaceous gout also known as Harrison syndrome. Not to be confused with Harrison internal medicine.
This is getting ridiculous. What’s the most common location? Pip and mtp of the joints in your hand. Oh, is this similar to osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis? It’s similar to rheumatoid arthritis and that’s why both of them are inflammatory. No duh. What is the second most common location? Ear penna and elbow. If you just say ear penna to your professor, he or she will be so happy they will take you to dinner.
What are these tofi? Hard yellowish white chalky nodules. These are not nodules like soft nodules like those in rheumatoid? No, these are rocky nodules because they are full of freaking crystals. Since this is chronic gout, expect to see a granuloma with multi.
That comes on suddenly and abruptly needs to be seen by a physician in the first 24 hours of its onset. Your doctor will immediately prescribe you medications that alleviate your acute gout attack or the immediate swelling and pain caused by the sharp increase in your uric acid levels. But that’s not where the treatment phase ends. We need to also treat the actual cause of the gout attack, the high levels of uric acid in blood, to prevent the chronic effects of gout.
Remember, uric acid is the compound in the body responsible for the development of gout and is a natural product of breakdown of many foods and even cells in our body. This video will cover the medications that can be prescribed to you to keep your uric acid level down and maintain it there in someone that has large deposits of gout in the body called Tofi, has at least two attacks of gout per year and has chronic kidney disease or a history of kidney stones composed of uric acid, we must start them on a uric acid lowering therapy.
The goal is to lower down the uric acid level to at least less than six and maintain it there. This is what decreases the existing burden of uric acid and prevents more uric acid from building up in the joints and damaging them. The following are options for urate lowering therapy. It is important to know that all of these agents can put you at risk for a gout flare, particularly when they are first started due to shifts in the uric acid level.
Alipurinol is a wellestablished and commonly used drug and is one of the first line treatments for gout. It is under the class of santhein oxidase inhibitors. These work by decreasing uric acid production and is widely available, efficacious and affordable. Side effects include gastrointestinal distress, rashes, and a rare but severe type of allergic reaction called Stevens Johnson’s syndrome and alupurnol hypersensitivity syndrome.
The latter has been implicated in patients with renal impairment and concurrent use of diuretics such as thiazides and is more common in people of certain ethnic background. Fibucistat is from the same class of drug as alupurinol and is a santine oxidase inhibitor as well. It is well tolerated, comparable in efficacy to alupurinol, and safe in patients with renal impairment. Side effects include diarrhea, nausea and elevation of liver enzymes.
Increased gal flares have been reported with high doses and is usually expected in the first month of treatment. Probenicid is a uric acuric agent. Uric acurics are the second class of uric acid lowering treatment. They lower uric acid levels through increased excretion in the kidneys. These agents increase the risk of uric acid stones and is contraindicated in those with a history of kidney stones. It can be used alone or as an adjunct to santine oxidase inhibitors.
Allergic reactions can occur with probenicid and should be used with caution in patients with g six, PD deficiency and peptic ulcer disease. Several drug interactions also exist whereby concurrent use of provenicid may increase blood levels of drugs or diminish their efficacy. Lisnerad is a recently approved uric acuric which increases uric acid excretion by working on the uric acid transporters in the kidneys. It is approved for use in combination with a santine oxidase inhibitor such as alipurinol for hyperuricemia.
It has shown to decrease dofus formation and lower likelihood of gout. Flares associate with sustained decrease in serum uric acid. Most common adverse effects include headache, influenza and reflux disease. It can also increase creatinine levels. Renal stones and other renal related adverse events have occurred. Duzalo this is the newest gout treatment which has become available in the market and it combines both alupurinol and nysinorad in one pill.
This is indicated in patients who have not achieved the goal level of uric acid from alupurinol alone. The most common adverse effects were headaches, influenza and increased creatinine levels as well as reflux. Similar to side effects from the individual components of aluprinol and lysinerat. Figloticase is a recombinant enzyme that breaks down uric acid in the body into a form that is easily excretable in the urine.
This medication is given as an iv infusion every two weeks and is approved by the FDA for Gout that is refractory to conventional treatment, including with deforming sulfacious gout. This medication can lead to a rapid reduction in uric acid burden in the body and faster dissolution of ToFi and can be used in patients with renal and liver impairments. However, infusion reactions and development of antibodies against the medication leading to a loss of efficacy can occur.
Patients should not be on any other urate lowering agent at the time of infusions, and close monitoring of the serum uric acid level should be done prior to each infusion. If a uric acid of greater than six is seen twice before subsequent infusions, it is recommended that the infusions be stopped so as to prevent side effects.
Can you see how treating the acute gout attack is equally as important as lowering the uric acid level in your body? There are many different types of medications out there for treating both, but your doctor will find the perfect solution based on your medical analysis, gout is a disease that is treatable but requires good compliance in a motivated patient. Go To Home